Rapid Clinical Response at Week 61,2*†
INDUCTION STUDY
AT 6 WEEKS
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
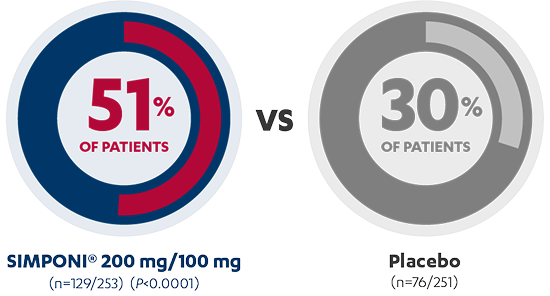

Sustained Clinical Response Through Week 541,3*†‡
MAINTENANCE STUDY
AT 54 WEEKS
PRIMARY ENDPOINT


Rapid improvement in endoscopic appearance at Week 61,2*†
INDUCTION STUDY: Major Secondary Endpoint
42% of patients taking SIMPONI® demonstrated an improvement in endoscopic appearance of mucosa vs 29% of patients receiving placebo (P=0.0014)


SIMPONI® 200 mg/100 mg (n=107/253)


PLACEBO (n=72/251)
View Study Designs*See complete study design for endpoint definitions and trial details.
†Patients who had a prohibited change in concomitant UC medication, an ostomy or colectomy, discontinued trial agent due to lack of therapeutic effect, or a dose adjustment (in maintenance study) were considered not to be in clinical response, clinical remission, or to have an improvement in endoscopic appearance of the mucosa from the time of the event onward.
‡Among Week 6 responders.
PURSUIT Study Designs
PURSUIT: Program of Ulcerative Colitis Research Studies Utilizing an Investigational Treatment.2,3
Access the full PURSUIT studies at Gastroenterology here:
INDUCTION STUDY
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of SIMPONI® (golimumab) in a Phase 2 and Phase 3 trial (N=761), designed as a randomized, dose-finding, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial conducted in patients with moderately to severely active UC who had an inadequate response or were intolerant to conventional therapy.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
Patients presented with a Mayo score between 6 and 12, and an endoscopic subscore of ≥2, and had failed or were intolerant of oral corticosteroids, oral 5-aminosalicylates (5-ASA), 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), azathioprine (AZA), were corticosteroid dependent.
TREATMENT REGIMEN
Patients were randomized and treated to the following at Weeks 0 and 2, respectively: SIMPONI® 100 mg to 50 mg, SIMPONI® 200 mg to 100 mg, SIMPONI® 400 mg to 200 mg, or placebo.
EFFICACY ENDPOINTS
Primary endpoint was clinical response at Week 6. Clinical response was defined as a decrease from baseline in the Mayo score of ≥30% and ≥3 points, accompanied by a decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1. Secondary endpoints included remission and endoscopic improvement of the mucosa at Week 6 (with a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1). Final efficacy evaluations were completed at Week 6.
MAINTENANCE STUDY
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of SIMPONI® (N=456) through Week 54 in a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter withdrawal study.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
Patients must have demonstrated clinical response to SIMPONI® in the PURSUIT induction study.
TREATMENT REGIMEN
Patients were randomized to receive SIMPONI® 50 mg, SIMPONI® 100 mg, or placebo, administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks.
EFFICACY ENDPOINTS
Primary endpoint was maintenance of clinical response through Week 54. Patients were assessed for UC disease activity based on partial Mayo score every 4 weeks; loss of response was confirmed by endoscopy. Patients had to maintain clinical response at every evaluation through Week 54 without demonstrating loss of response at any point to be considered in response in the SIMPONI® 100-mg group compared with the placebo group. Secondary endpoint was clinical remission at Week 30 and Week 54.
Both studies permitted concomitant treatment with stable doses of 5-ASA, corticosteroids, and/or immunomodulators. However, corticosteroids were to be tapered at the start of the maintenance study in patients in clinical response at Week 6.
Demonstrated Safety Profile of SIMPONI® in the PURSUIT Clinical Trials
In the Phase 2/3 trials in UC evaluating 1233 SIMPONI®-treated patients, no new adverse drug reactions were identified, and the frequency of adverse drug reactions was similar to the safety profile observed in patients with RA, PsA and AS.1
| Placebo*† (N=156) | golimumab 100 mg* (N=154) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean duration of follow-up period, wk | 32.7 | 46.3 |
| Mean exposure, no. of injections | 8.2 | 11.3 |
| ≥1 Adverse event, n (%) | 103 (66.0) | 113 (73.4) |
| Frequent adverse events,‡ n (%) | ||
| UC | 29 (18.6) | 24 (15.6) |
| Naso- pharyngitis | 11 (7.1) | 21 (13.6) |
| Headache | 14 (9.0) | 12 (7.8) |
| Arthralgia | 12 (7.7) | 8 (5.2) |
| Abdominal pain | 4 (2.6) | 11 (7.1) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 4 (2.6) | 9 (5.8) |
| Rash | 3 (1.9) | 7 (4.5) |
| Pharyngitis | 4 (2.6) | 5 (3.2) |
| Cough | 5 (3.2) | 9 (5.8) |
| ≥1 Infection,§ n (%) | 44 (28.2) | 60 (39.0) |
| Required anti- microbial therapy | 24 (15.4) | 44 (28.6) |
| Dis- continued study agent as a result of ≥1 adverse event,|| n (%) | 10 (6.4) | 14 (9.1) |
| ≥1 Serious adverse event, n (%) | 12 (7.7) | 22 (14.3) |
| Neoplasm benign, malignant, and unspecified (including cysts and polyps), n (%) | 1 (0.6) | 4 (2.6) |
| Total number of study agent injections | 3333 | 4440 |
| Injections with injection-site reactions | 18 (0.5) | 28 (0.6) |
| ≥1 Injection-site reactions, n (%) | 3 (1.9) | 11 (7.1) |
*Includes data up to the time of dose adjustment for those who increased dose.
†Patients who were in clinical response to golimumab induction dosing and were randomized to placebo on entry into this maintenance trial.
‡Frequent adverse events are those that occurred at a rate of ≥5% in any treatment group.
§Infection as assessed by the investigator.
||UC flares were the most frequently reported adverse event that led to discontinuation of study agent in 1.9%, 3.9%, and 4.5% of patients in the placebo, golimumab 50-mg, and golimumab 100-mg groups, respectively.